A closed system can exchange energy eg. Different types of systems are generally characterized by different sets of variables.

Lesson 4 Thermodynamic Systems And Processes Describe The Following Types Of Thermodynamic Systems Isolated System Closed System Open System Define Ppt Download
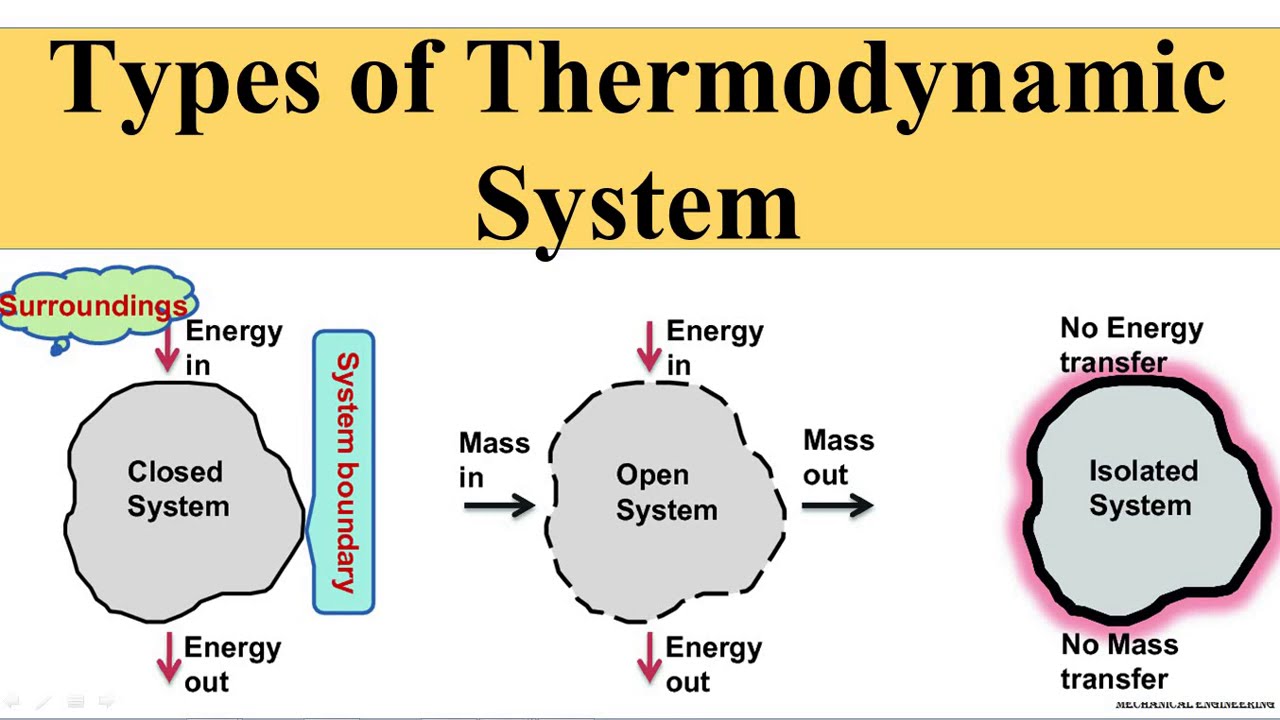
It is a system in which there is only energy interaction takes place but not mass interaction.

. The mass inside the closed system remains constant. It is embedded in its surroundings or environment. In reality the immediate surroundings of the system are interacting.
Heat but not matter. When any of the properties of the system such as temperature pressure volume etc change the sytem is said to have undergone thermodynamic process. 1Closed system 2Open system 3Isolated system.
Isochoric process in which the volume V is kept constant ΔV 0. A system in which the transfer of energy but not mass can takes place across the boundary is called closed system. Adiabatic process in which the heat transfer is zero Q0.
There are Four types of Thermodynamic. A closed system can exchange energy eg. The thermodynamic state of a system is defined by specifying values of a set of measurable properties sufficient to determine all other properties.
Definition of Thermodynamic Equilibrium. B adiabatic where no heat is exchanged by the system. The state of a system can change as a result of its interaction with the environment.
On the basis of mass and energy transfer the thermodynamic system is divided into three types. The Four Types of Thermodynamic Processes The four types of thermodynamic process are isobaric isochoric isothermal and adiabatic. It is a system in which both mass interaction as well as energy interaction takes place.
Isothermal process adiabatic process ischoric process isobaric process and reversible process. For example the thermodynamic variables for a stretched rubber band are tension length temperature and mass. Various types of thermodynamic processes are.
What is a steady flow process. Thermodynamic System Types of Systems and Definition. Isobaric process in which the pressure P is kept constant ΔP 0.
What do you mean by quasi-static process. Heat but not matter. Prove that for an isolated system there is no change in.
Systems under Pressure and Temperature equilibrium but not under chemical equilibrium are said to be in meta-stable equilibrium condition. For fluid systems typical properties are pressure volume and temperature. Isothermal process in which the temperature T is kept constant ΔT 0.
C isobaric where the systems pressure is constant. Thermodynamic system is basically defined as the finite quantity of matter or prescribed region in. Heat and the thermodynamics play an important role in helping process designers and engineers optimize their processes.
More complex systems may require the specification of more unusual properties. Types of Thermodynamic Equilibrium with Example. In case of closed system in thermodynamics there will not be any.
Types of Thermodynamic System. A wall of a thermodynamic system may be purely notional when it is described as being permeable. It also helps them to harness the energy associated with chemical reactions economically.
3 The Concept of a State. A study object is a substance with a large number of molecules or atoms. 1-Open System 2-Closed System 3-Isolated System An open system can exchange matter and energy.
The system in which the transfer of mass as well as energy can take place across its boundary is called as. There are two types of interaction in the thermodynamic system. It is the energy that kinetic energy of the molecules of the substance possessed.
Name the different types of system. A thermodynamic system is a body of matter andor radiation confined in space by walls with defined permeabilities which separate it from its surroundings. It can exchange heat with and do work on its environment through a boundary which is the imagined wall that separates the system and the environment Figure 32.
Types of Thermodynamic System. All these have been described below. Classes of thermodynamic system.
An Open system is defined as the system in which there is the transfer of mass and energy between system and surrounding. A thermodynamic system includes anything whose thermodynamic properties are of interest. A system contains what is called a study object.
Real or imaginary walls can define this limit. There are three types of thermodynamic system. On the basis of mass and energy transfer the thermodynamic system is divided into three types.
Open system closed system and isolated system. Now lets look at the types of a thermodynamic system. And d isochoric where the systems volume is constant.
The surroundings may include other thermodynamic systems or physical systems that are not thermodynamic systems. A thermodynamic system is three types. There are several types of thermodynamic processes including a isothermal where the systems temperature is constant.
Explain homogeneous and heterogeneous system. Thermodynamics define heat as the energy in transit. A thermodynamic system is a part of the physical universe with a specific limit for observation.
The change in a system can be fast or slow and large or small. There are three types of thermodynamic system. In Thermodynamics types of processes include.
1-Open System 2-Closed System 3-Isolated System An open system can exchange matter and energy. A system is said to be in equilibrium if it does not tend to undergo any change. In thermodynamic there are three types of system available.
WHAT IS THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEM SURROUNDINGS AND BOUNDARY. A system in which the transfer of energy but not mass can takes place across the boundary is called a closed system. The system in which the transfer of energy takes place across its boundary with the surrounding but no.
Those terms are pretty hard to understand just from the names.

Thermodynamic System Types Of Thermodynamic System Mechanical Booster

0 Comments